Spout is a protocol which allows you to share a video texture on your GPU between two programs this means that it is zero-latency and zero-compression. Spout works with alpha channel but not audio.
You can live-stream to Unreal Engine via Spout either into a Render Target or in to Unreal's Media Framework which can be used with nDisplay, Composure, Media Plate and other useful tools:
Instantly Input with the Media Input Wizard:
- In the Off World Live Unreal Editor drop down select the Media Input Wizard:
- In the window that opens:
- Select Spout as your input format.
- You need an active Spout Sender to receive, such as from OBS Studio. You can select this from the list or refresh if you don't see it.
- You can select between three options of how to receive the texture:
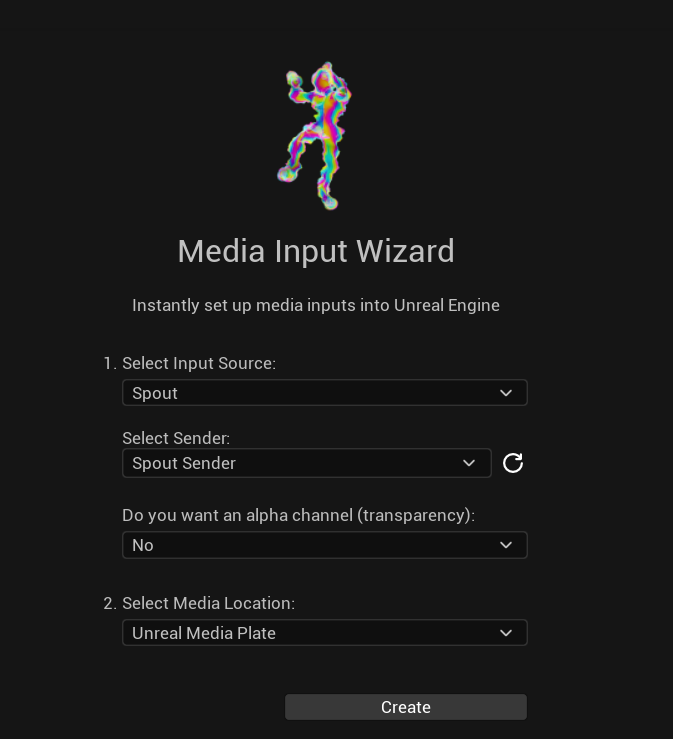
- Media Plate: This is Unreal's media plate which avoids anti-aliasing. We recommend this option if you want clean media in your scene. This uses the Media Framework Spout input below.
- Material: This is to an Unreal material which you can use as you like in your scene. This uses the Render Target input below.
- Plane: This is to a standard Unreal plane. This will have ghosting on it due to Unreal post processing so we recommend the Media Plate unless you need a plane for a specific reason. This uses the Render Target input below.
- Click create and the sender will automatically be generated in your scene.
Use Unreal Media Framework to Input Spout into nDisplay, Composure, etc
Spout can now be received via an Actor created in the Content Browser, which is compatible with Media Plate, Composure and nDisplay workflows.
- To add a Media source right click the Content Browser and select Spout Source:
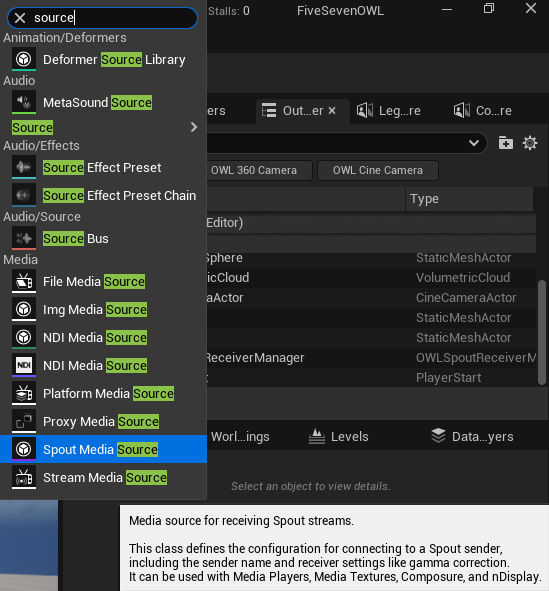
- This will create a Spout Media Source Actor. Click to access it’s properties.

- Use the Spout Sender Name dropdown to select a Spout source from the list of active sources. If you don't select it will just use the first available active sender. Use the refresh button if a new source has been initiated since the Spout Media Source Actor has been open.
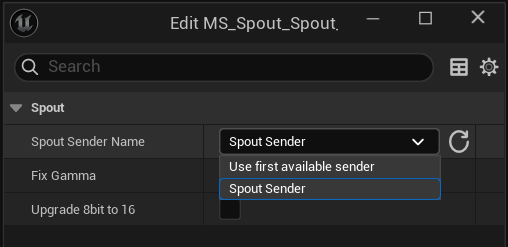
- Use the Fix Gamma Checkbox for media sources that are in a different colorspace to UE’s default sRGB colorspace. Quicktime video are an example of media sources that can be fixed with this option. This helps ensure proper color reproduction when receiving from external applications. Keep this unticked if you want to use the Spout input as data such as from TouchDesigner.
- Convert 8-bit textures to 16-bit format for better color precision.
Useful when working with HDR workflows or when higher precision is needed.
- Dragging the OWL Spout Media Source Directly in to the viewport will create a new Unreal Media Plate Actor with the Source already assigned. Click the Open button in the Details panel of the Media plate to view the Source:
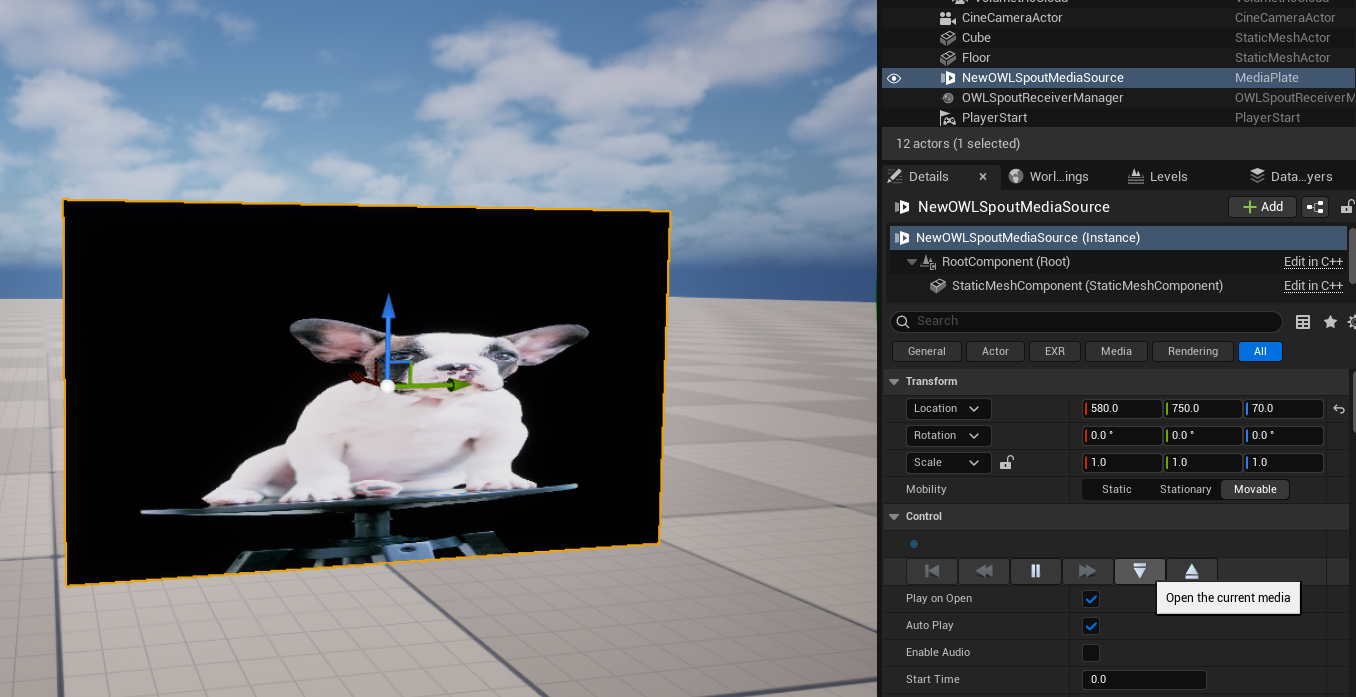
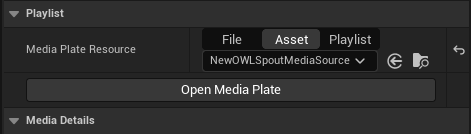
- If you want to add the Spout input as a Source to an existing Unreal Media Plate then navigate to the media Plate’s Details panel, find the Playlist Section, ensure the Media Plate resource is set to Asset and then select the Spout Source from the dropdown:
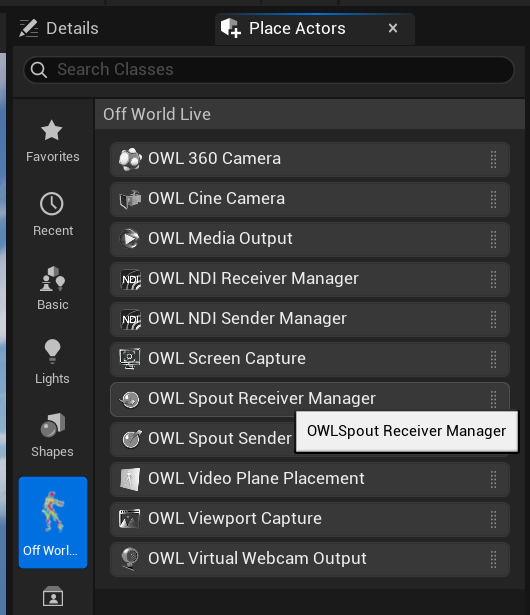
Use the OWL Spout Receiver Manager to receive Spout to a Render Target
- In World Outliner select OWLSpoutReceiverManager so it opens in your Details panel.
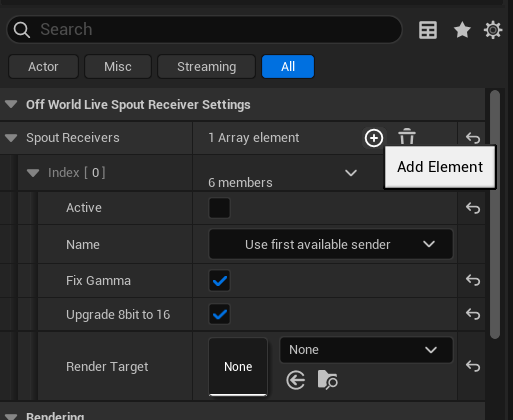
- Add a Spout Receiver Array Element and click the arrow in the right hand corner to open the Array Element showing its Members:
- Create a Render Target and give it a name.
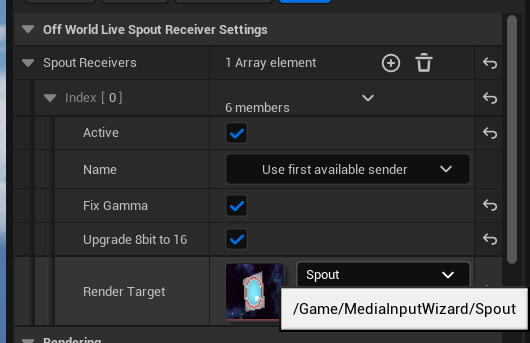
- Select a Spout input feed from the list of options in the Name dropdown (any active Spout source will show) and Click Active to start capturing the Spout source to your Render Target.
- Select 'Fix Gamma' if you want to convert the gamma to Unreal's working color space. Keep this unticked if you want to use the Spout input as data such as from TouchDesigner.
- Convert 8-bit textures to 16-bit format for better color precision.
Useful when working with HDR workflows or when higher precision is needed. - If you want to apply your Render Target to your scene, then right click on it to create a Material which you can drag-and-drop onto any Unreal Actor (or just generate this automatically using the Wizard as described above).
Additional Features
- To receive multiple input feeds, just add additional Array Elements.
- You can control the Active tick-box via Blueprints to manage which cameras are rendering simultaneously and so reduce computational load.